You are going to build a stone wall. The wall should be straight and N meters long, and its thickness should be constant; however, it should have different heights in different places. The height of the wall is specified by an array H of N positive integers. H[I] is the height of the wall from I to I+1 meters to the right of its left end. In particular, H[0] is the height of the wall's left end and H[N−1] is the height of the wall's right end.
The wall should be built of cuboid stone blocks (that is, all sides of such blocks are rectangular). Your task is to compute the minimum number of blocks needed to build the wall.
Write a function:
class Solution { public int solution(int[] H); }
that, given an array H of N positive integers specifying the height of the wall, returns the minimum number of blocks needed to build it.
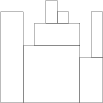
For example, given array H containing N = 9 integers:
H[0] = 8 H[1] = 8 H[2] = 5 H[3] = 7 H[4] = 9 H[5] = 8 H[6] = 7 H[7] = 4 H[8] = 8
the function should return 7. The figure shows one possible arrangement of seven blocks.
Assume that:
- N is an integer within the range [1..100,000];
- each element of array H is an integer within the range [1..1,000,000,000].
Complexity:
- expected worst-case time complexity is O(N);
- expected worst-case space complexity is O(N), beyond input storage (not counting the storage required for input arguments).
난이도가 easy 입니다
하지만 전 어려워서 여기 저기 찿아보고 문제도 한참 이나 지난후 이해할수 있었습니다.
쌓을 벽돌이 이전 벽돌보다 크면 문제 없습니다.
하지만 쌓을 벽돌이 이전벽돌보다 작으면 쌓을 벽돌보다 큰 이전 벽돌을 없앱니다. 쌓을벽돌보다 같거나 작은게 나올때까지요.
쌓을 벽돌보다 같은게 나오면 blockCnt 에 해당이 안되겠지요?
알고리즘은 위와 같습니다.
// you can also use imports, for example: // import java.util.*; import java.util.Stack; // you can write to stdout for debugging purposes, e.g. // System.out.println("this is a debug message"); class Solution { public int solution(int[] H) { // write your code in Java SE 8 Stack<Integer> stack = new Stack(); int blockCnt = 0; for(int i =0 ; i < H.length; i++){ while(stack.size() > 0 && stack.peek() > H[i]){ stack.pop(); } if(stack.size() == 0 || stack.peek() < H[i]){ stack.push(H[i]); blockCnt++; } } return blockCnt; } }
'프로그래밍 > 알고리즘' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 시간 복잡도 (0) | 2018.04.21 |
|---|---|
| [Codility] CountSemiprimes (0) | 2018.04.21 |
| [Codility] cyclicRotation (0) | 2018.04.15 |
| [Codility] Binary Gap 알고리즘 (0) | 2018.04.14 |
| 알고리즘 공부 사이트 (0) | 2017.01.27 |




