Play game 누르시고 기다리시면 됩니다.
인트로 끝나면 게임 할수 있습니다.
'플래시 게임 > 액션' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 디펜스게임 ㅡ트리니타스- (0) | 2018.06.13 |
|---|---|
| 스트리트 파이터2 (0) | 2017.01.21 |
| 메탈 슬러그 (0) | 2017.01.13 |
Play game 누르시고 기다리시면 됩니다.
인트로 끝나면 게임 할수 있습니다.
| 디펜스게임 ㅡ트리니타스- (0) | 2018.06.13 |
|---|---|
| 스트리트 파이터2 (0) | 2017.01.21 |
| 메탈 슬러그 (0) | 2017.01.13 |
양도세 계산은 양도차익 즉 '양도가액 - 취득가액 - 필요경비'를 계산해 나온 이익에 대해 과세합니다.
이 경우 양도세 절세를 위해 필요경비를 어디까지 인정받느냐가 매우 중요한데요
오늘은 그 중에서 집수리비에 대해 알아보겠습니다.
세법과 회계에서는 수리 또는 수선을 다음과 같은 기준을 통해 전혀 다른 판단을 합니다.
1. 수리 또는 수선을 해서 건물등의 내용연수가 연장했는가? (즉, 건물등이 사용될 수 있는 기간을 연장시킬만한 수리였는가?)
2. 또는 그 건물등의 가치를 증가시켰는가? (즉, 그 공사로 인해 건물등의 시가가 올라갔는가?)
이 두 기준중 하나라도 부합된다면 이를 '자본적 지출'이라 하여 회계에선 건물가액에 포함하며, 이 기준에 부합되지 않는 경우에는 '수익적 지출'이라 하여 당해 비용으로 처리합니다.
양도세법에서는 위에서 본 자본적지출 즉, 공사로 인해 건물등의 사용기간이 늘거나 가격이 인상되었을 때와 추가로 그 건물등의 용도변경 · 개량 또는 이용편의를 위해 지출한 비용에 대해 증빙서류로 실제 지출한 사실이 확인되는 경우 필요경비로 공제가능합니다.
그럼 실제 사례를 통해 살펴 보겠습니다.
1. 베란다 샤시, 방 확장등 내부시설 및 거실 인테리어 공사 : 내부시설 개량을 위한 것으로서 공제가능(심판청구 2001서1140,20011018)
2. 싱크대교체 및 수도꼭지 교체 와 화장실 변기교체 : 자본적 지출도 아니며, 개량등을 위한 것도 아니므로 공제불가(심사청구 양도 2008-0086,20080630)
3. 주방가구비용 및 도배공사 그리고 화장실 공사 : 수선비 성경의 수익적 지출에 해당되므로 공제불가(심판청구 2006서0062,20060509)
4. 지역난방에서 중앙난방으로 보일러시설 교체공사 : 자본적지출로 공제가능
사례를 보니 더 어렵다고요?
위 사례들은 판례의 일부일 뿐이며, 100% 그대로 적용된다고 할 수는 없습니다만, 그래도 가이드라인은 설정해 줄 수 있습니다.
예를 들어 화장실공사를 하는데 안방을 줄이고 그 안에 화장실과 간이 샤워실을 놓았다면, 자본적지출이라 할 수도 있고 이용편의 또는 개량을 위한 지출이므로 공제가능하겠죠
하지만 단지 변기교체 및 욕조 교체라면 공제받기는 힘들거구요
이상 공제가능한 수선과 불가한 수선에 대한 설명을 드렸습니다만, 가장 중요한 것은 지급내역 즉, 영수증 또는 계약서 등의 지급증빙을 잘 보관하는 것이겠죠
공사관련 증빙은 계약서, 견적서, 세금계산서등이 있을 수 있겠고, 대금지급증빙으로서는 입금증, 신용카드영수증, 현금영수증등이 있겠네요
공사관련 증빙과 대금지급증빙 다 있어야 하냐구요?
움~~~~ 왠만하면 다 있는게 좋겠죠
여기서 자주 묻는 질문과 답
1. 공사업체에서 세금계산서 받으려면 10% 더 주라는데요?
☞ 10% 부가세 주고받는 건 정상적인것인데... ㅎㅎ 움... 아끼실 수는 있겠네요 간이영수증이라도 받으세요 대신 계좌이체등을 통해 지급사실은 명확히 해 두시구요 움... 간이영수증도 안 주면... 계약서나 견적서라도 받으시구요 그리고 중요한것!! 그 업체의 사업자등록번호는 꼭 알아야 합니다.
2. 세금계산서의 품목에인테리어라고만 되어 있습니다. 공제가능한가요?
☞ 위에서 설명한 기준에 해당된다면요... 제 아시는 분이 한 10여년전에 그러시더군요 그냥 인테리어라고 되어 있다면 세무서에서 어떤 공사인지 어떻게 알겠냐고 그래서 이것저것 귀찮아 자신은 인테리어라고 품목을 적어 받는다고... ㅎㅎ
3. 간이영수증을 받았어요 그런데 사업자등록번호가 없네요 공제가능한가요?
☞ 공사한 업체의 주민등록번호라도 아시나요? 모르시다면 공제불가능할 것 같습니다.
4. 실제 공사는 베란다공사와 함께 화장실공사을 했습니다. 헌데 세금계산서의 품목란에 화장실 공사 및 마루공사외 이렇게만 나와있습니다. 공제가능한가요?
☞ 움... 어려울 수도 있겠는데요
공제대상 공사와 불공제대상 공사가 섞여있는 듯 한데요
견적서라도 다시 받으시는게 좋을 듯 합니다.
마지막으로 양도관련 상담은 실제 증빙과 자료를 보고 할 때 가장 정확한 답이 나옵니다.
여러분께 가장 좋은 세무상담자는 바로 가까운 곳에 있는 세무사라고 전에도 말씀드렸구요
인터넷이나 전화상담만 하시지 마시고 돈 몇 푼 아낄려다 나중에 낭패를 볼 수도 있는바, 꼭 가까운 곳에 있는 세무사사무실을 방문해 자세한 상담을 받아보시기 바랍니다.
| 부동산 전세 계약시 주의사항 (0) | 2018.06.13 |
|---|
Common AspectJ annotations :
See directory structure of this example.
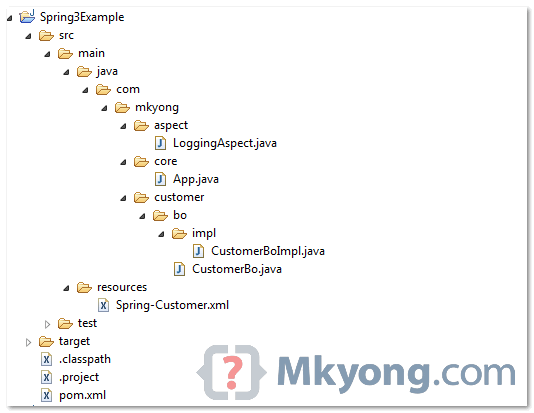
To enable AspectJ, you need aspectjrt.jar, aspectjweaver.jar and spring-aop.jar. See following Maven pom.xml file.
File : pom.xml
<project ...>
<properties>
<spring.version>3.0.5.RELEASE</spring.version>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-core</artifactId>
<version>${spring.version}</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-context</artifactId>
<version>${spring.version}</version>
</dependency>
<!-- Spring AOP + AspectJ -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-aop</artifactId>
<version>${spring.version}</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.aspectj</groupId>
<artifactId>aspectjrt</artifactId>
<version>1.6.11</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.aspectj</groupId>
<artifactId>aspectjweaver</artifactId>
<version>1.6.11</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</project>Normal bean, with few methods, later intercept it via AspectJ annotation.
package com.mkyong.customer.bo;
public interface CustomerBo {
void addCustomer();
String addCustomerReturnValue();
void addCustomerThrowException() throws Exception;
void addCustomerAround(String name);
}package com.mkyong.customer.bo.impl;
import com.mkyong.customer.bo.CustomerBo;
public class CustomerBoImpl implements CustomerBo {
public void addCustomer(){
System.out.println("addCustomer() is running ");
}
public String addCustomerReturnValue(){
System.out.println("addCustomerReturnValue() is running ");
return "abc";
}
public void addCustomerThrowException() throws Exception {
System.out.println("addCustomerThrowException() is running ");
throw new Exception("Generic Error");
}
public void addCustomerAround(String name){
System.out.println("addCustomerAround() is running, args : " + name);
}
}In Spring configuration file, put “<aop:aspectj-autoproxy />“, and define your Aspect (interceptor) and normal bean.
File : Spring-Customer.xml
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-3.0.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop-3.0.xsd ">
<aop:aspectj-autoproxy />
<bean id="customerBo" class="com.mkyong.customer.bo.impl.CustomerBoImpl" />
<!-- Aspect -->
<bean id="logAspect" class="com.mkyong.aspect.LoggingAspect" />
</beans>In below example, the logBefore() method will be executed before the execution of customerBo interface,addCustomer() method.
File : LoggingAspect.java
package com.mkyong.aspect;
import org.aspectj.lang.JoinPoint;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Before;
@Aspect
public class LoggingAspect {
@Before("execution(* com.mkyong.customer.bo.CustomerBo.addCustomer(..))")
public void logBefore(JoinPoint joinPoint) {
System.out.println("logBefore() is running!");
System.out.println("hijacked : " + joinPoint.getSignature().getName());
System.out.println("******");
}
}Run it
CustomerBo customer = (CustomerBo) appContext.getBean("customerBo");
customer.addCustomer();Output
logBefore() is running!
hijacked : addCustomer
******
addCustomer() is runningIn below example, the logAfter() method will be executed after the execution of customerBo interface, addCustomer()method.
File : LoggingAspect.java
package com.mkyong.aspect;
import org.aspectj.lang.JoinPoint;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.After;
@Aspect
public class LoggingAspect {
@After("execution(* com.mkyong.customer.bo.CustomerBo.addCustomer(..))")
public void logAfter(JoinPoint joinPoint) {
System.out.println("logAfter() is running!");
System.out.println("hijacked : " + joinPoint.getSignature().getName());
System.out.println("******");
}
}Run it
CustomerBo customer = (CustomerBo) appContext.getBean("customerBo");
customer.addCustomer();Output
addCustomer() is running
logAfter() is running!
hijacked : addCustomer
******In below example, the logAfterReturning() method will be executed after the execution of customerBo interface,addCustomerReturnValue() method. In addition, you can intercept the returned value with the “returning” attribute.
To intercept returned value, the value of the “returning” attribute (result) need to be same with the method parameter (result).
File : LoggingAspect.java
package com.mkyong.aspect;
import org.aspectj.lang.JoinPoint;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.AfterReturning;
@Aspect
public class LoggingAspect {
@AfterReturning(
pointcut = "execution(* com.mkyong.customer.bo.CustomerBo.addCustomerReturnValue(..))",
returning= "result")
public void logAfterReturning(JoinPoint joinPoint, Object result) {
System.out.println("logAfterReturning() is running!");
System.out.println("hijacked : " + joinPoint.getSignature().getName());
System.out.println("Method returned value is : " + result);
System.out.println("******");
}
}Run it
CustomerBo customer = (CustomerBo) appContext.getBean("customerBo");
customer.addCustomerReturnValue();Output
addCustomerReturnValue() is running
logAfterReturning() is running!
hijacked : addCustomerReturnValue
Method returned value is : abc
******In below example, the logAfterThrowing() method will be executed if the customerBo interface,addCustomerThrowException() method is throwing an exception.
File : LoggingAspect.java
package com.mkyong.aspect;
import org.aspectj.lang.JoinPoint;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.AfterThrowing;
@Aspect
public class LoggingAspect {
@AfterThrowing(
pointcut = "execution(* com.mkyong.customer.bo.CustomerBo.addCustomerThrowException(..))",
throwing= "error")
public void logAfterThrowing(JoinPoint joinPoint, Throwable error) {
System.out.println("logAfterThrowing() is running!");
System.out.println("hijacked : " + joinPoint.getSignature().getName());
System.out.println("Exception : " + error);
System.out.println("******");
}
}Run it
CustomerBo customer = (CustomerBo) appContext.getBean("customerBo");
customer.addCustomerThrowException();Output
addCustomerThrowException() is running
logAfterThrowing() is running!
hijacked : addCustomerThrowException
Exception : java.lang.Exception: Generic Error
******
Exception in thread "main" java.lang.Exception: Generic Error
//...In below example, the logAround() method will be executed before the customerBo interface, addCustomerAround()method, and you have to define the “joinPoint.proceed();” to control when should the interceptor return the control to the original addCustomerAround() method.
File : LoggingAspect.java
package com.mkyong.aspect;
import org.aspectj.lang.ProceedingJoinPoint;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Around;
@Aspect
public class LoggingAspect {
@Around("execution(* com.mkyong.customer.bo.CustomerBo.addCustomerAround(..))")
public void logAround(ProceedingJoinPoint joinPoint) throws Throwable {
System.out.println("logAround() is running!");
System.out.println("hijacked method : " + joinPoint.getSignature().getName());
System.out.println("hijacked arguments : " + Arrays.toString(joinPoint.getArgs()));
System.out.println("Around before is running!");
joinPoint.proceed(); //continue on the intercepted method
System.out.println("Around after is running!");
System.out.println("******");
}
}Run it
CustomerBo customer = (CustomerBo) appContext.getBean("customerBo");
customer.addCustomerAround("mkyong");Output
logAround() is running!
hijacked method : addCustomerAround
hijacked arguments : [mkyong]
Around before is running!
addCustomerAround() is running, args : mkyong
Around after is running!
******It’s always recommended to apply the least power AsjectJ annotation. It’s rather long article about AspectJ in Spring. for further explanations and examples, please visit the reference links below.